- Python Signal Example
- Signals Slots Python Games
- Python Signal Library
- Signals Slots Python Game
- Python Signal Windows
- Python Signal Kill
last modified July 16, 2020
Execution of Python signal handlers¶. A Python signal handler does not get executed inside the low-level (C) signal handler. Instead, the low-level signal handler sets a flag which tells the virtual machine to execute the corresponding Python signal handler at a later point(for example at the next bytecode instruction). Use Signals and Slots Editing Mode for connecting predefined Qt signals directly to predefined Qt slots. So for 'Close' button on a simple dialog, you can just drag a connection from the button to the dialog, select the clicked signal and the reject slot, click 'OK', and there would be nothing more to do.
In this part of the PyQt5 programming tutorial, we explore events and signalsoccurring in applications.
Events in PyQt5
GUI applications are event-driven. Events are generated mainly by theuser of an application. But they can be generated by other means as well; e.g. anInternet connection, a window manager, or a timer.When we call the application's exec_() method, the application entersthe main loop. The main loop fetches events and sends them to the objects.
In the event model, there are three participants:
- event source
- event object
- event target
The event source is the object whose state changes. It generates events.The event object (event) encapsulates the state changes in the event source.The event target is the object that wants to be notified. Event source objectdelegates the task of handling an event to the event target.
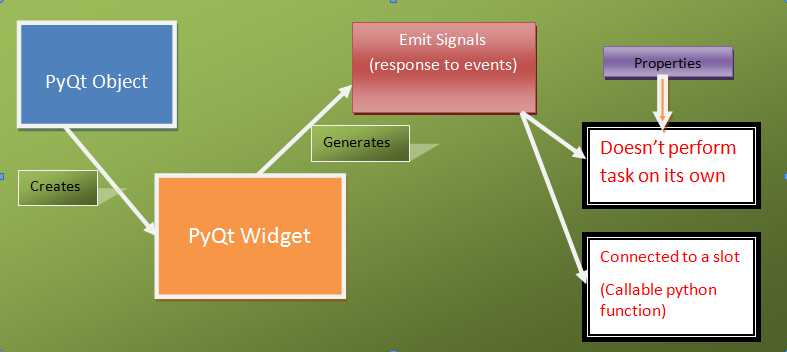
PyQt5 has a unique signal and slot mechanism to deal with events.Signals and slots are used for communication between objects. A signalis emitted when a particular event occurs. A slot can be any Python callable.A slot is called when its connected signal is emitted.
PyQt5 signals and slots
This is a simple example demonstrating signals and slots in PyQt5.
In our example, we display a QtGui.QLCDNumberand a QtGui.QSlider. We change the lcdnumber by dragging the slider knob.
Here we connect a valueChanged signal of the slider to thedisplay slot of the lcd number.
The sender is an object that sends a signal. The receiveris the object that receives the signal. The slot is the method thatreacts to the signal.
PyQt5 reimplementing event handler
Events in PyQt5 are processed often by reimplementing event handlers.
In our example, we reimplement the keyPressEvent() event handler.
If we click the Escape button, the application terminates.
Event object in PyQt5
Event object is a Python object that contains a number of attributesdescribing the event. Event object is specific to the generated eventtype.
Python Signal Example
In this example, we display the x and ycoordinates of a mouse pointer in a label widget.
The x and y coordinates are displayd in a QLabelwidget.
Signals Slots Python Games
Mouse tracking is disabled by default, so the widget only receives mouse moveevents when at least one mouse button is pressed while the mouse is being moved.If mouse tracking is enabled, the widget receives mouse move events evenif no buttons are pressed.
The e is the event object; it contains data about the eventthat was triggered; in our case, a mouse move event. With the x()and y() methods we determine the x and y coordinates ofthe mouse pointer. We build the string and set it to the label widget.
PyQt5 event sender
Sometimes it is convenient to know which widget is the sender of a signal.For this, PyQt5 has the sender method.
We have two buttons in our example. In the buttonClicked methodwe determine which button we have clicked by calling thesender() method.
Both buttons are connected to the same slot.
We determine the signal source by calling the sender() method.In the statusbar of the application, we show the labelof the button being pressed.
Python Signal Library
PyQt5 emitting signals
Signals Slots Python Game

Objects created from a QObject can emit signals.The following example shows how we to emit custom signals.
We create a new signal called closeApp. This signal isemitted during a mouse press event. The signal is connected to theclose() slot of the QMainWindow.
Python Signal Windows
A signal is created with the pyqtSignal() as a class attributeof the external Communicate class.
The custom closeApp signal is connected to the close()slot of the QMainWindow.
When we click on the window with a mouse pointer, the closeApp signalis emitted. The application terminates.
Python Signal Kill
In this part of the PyQt5 tutorial, we have covered signals and slots.